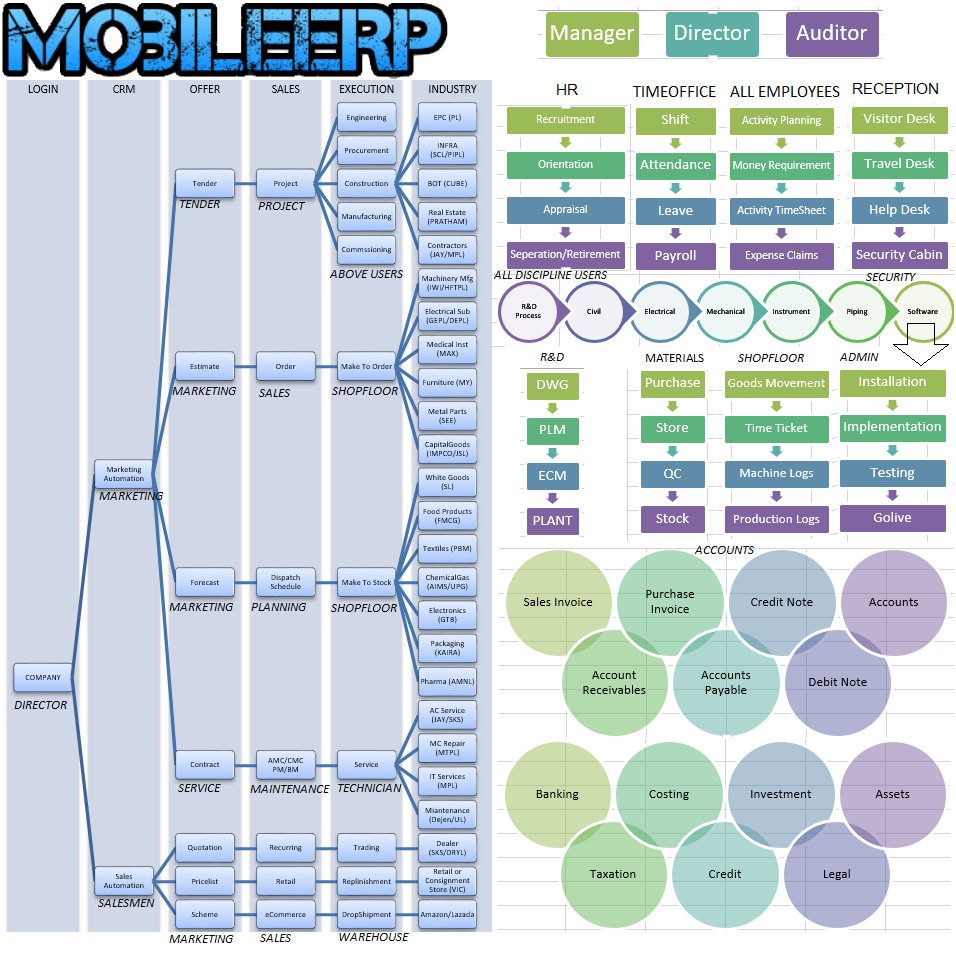
Make To Order
Manufacturing
Make To Stock
Manufacturing
Buy to Supply
Trading
Supply of Service
Services
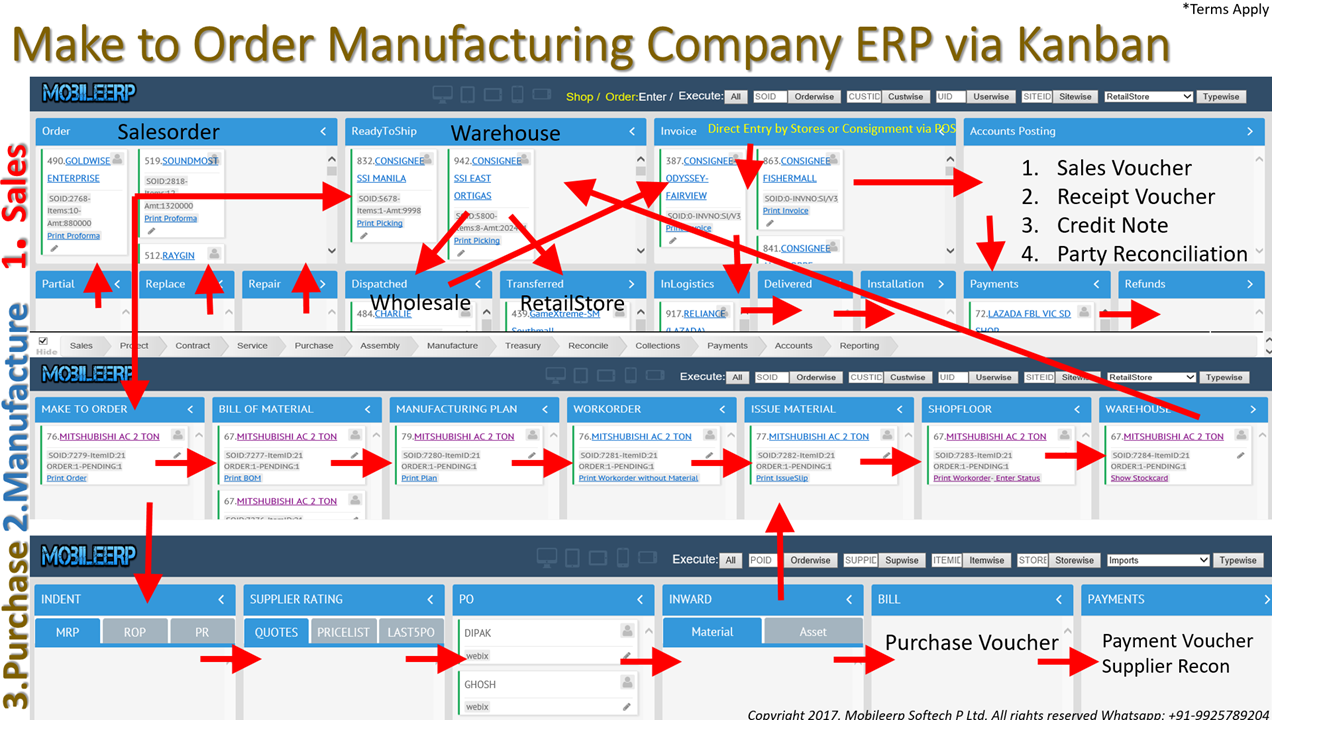



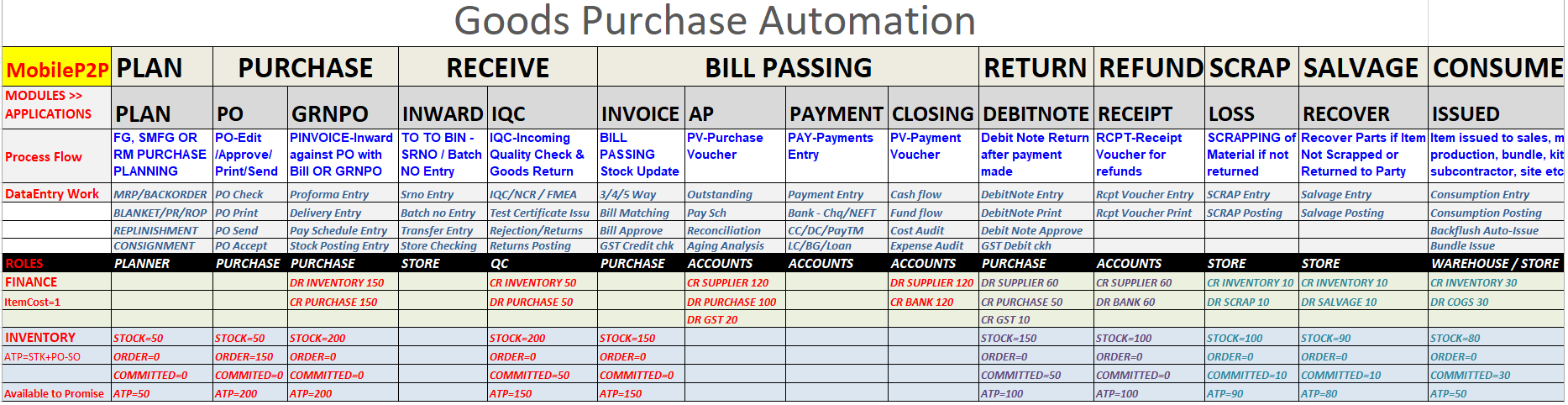


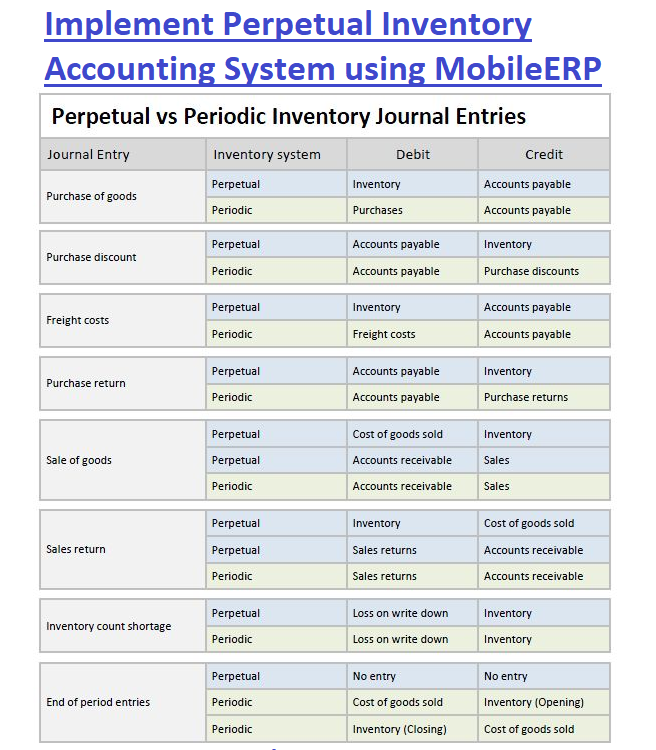
Implementation work for SCM Managers
TEAM
Suppliers
Stores
Factories
Subcons
Warehouse
Customers
TARGETS
Develops better customer relationship
Creates better delivery mechanisms
Minimises warehouse and transportation costs.
Enhances inventory management,
Minimising waste, rework, rejects
Make vs Buy Strategy optimization
GOALS
Rapid Demand Fulfillment
Give Customer what they want
Give Customer when they want
Minimization supply chain expenses
Reduce products and service costs
Keep system transparent
ACTIONS
Forecast/Plan Demand
Procurement
Production
Dispatch
Logistics
Returns
Simplify
1. Forecasting
2. Production
3. Procurement
4. Dispatch
5. Transportation
Automate
1. Forecasting
2. Production
3. Procurement
4. Dispatch
5. Transportation
Control
1. Production
2. Suppliers
3. Inventory
4. Delivery
5. Quality
Eliminate
1. Process bottlenecks
2. Rework/Repetitive Work
3. Delays in Delivery
4. Customer Complains
5. Customers Rejects
What is SCM?
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM), the management of the flow of goods and services, involves the movement and storage of raw materials, of work-in-process inventory, and of finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Key goals for supply chain management should be to achieve efficient fulfillment of demand, drive outstanding customer value, enhance organizational responsiveness, build network resiliency, and facilitate financial success.
A supply chain is comprised of all the businesses and individual contributors involved in creating a product, from raw materials to finished merchandise. ... Examples of supply chain activities include farming, refining, design, manufacturing, packaging, and transportation.
What are elements of SCM?
There are four major elements of supply chain management: integration, operations, purchasing and distribution. Each relies on the others to provide a seamless path from plan to completion as affordably as possible.