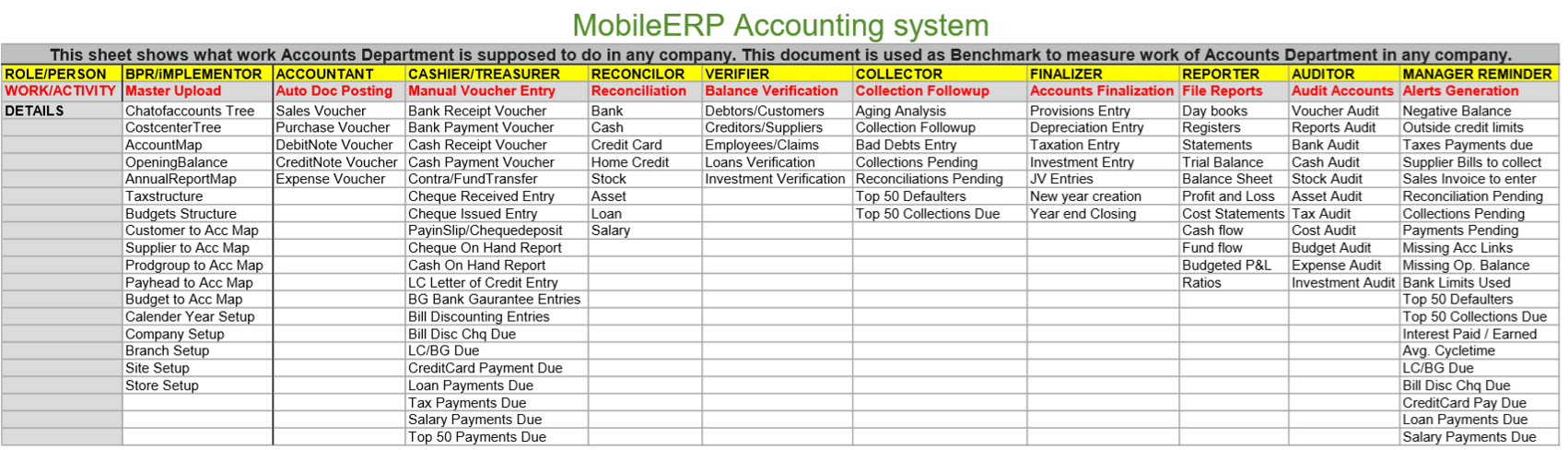
Create Invoice
28 different types
6 GST types
Invoice Approval
Reduce Stock if products
Create Sales Voucher
Audit Invoice
Sales Voucher wrt Invoice
Print/Send Sales Invoice
Invoice Analysis
Monitor Invoices
Monitor Payments

Plan

Do

Check

Act
What is o2c-Order to Cash cycle?
Order to Cash also known as O2C or OTC is the business process that covers the entirety of the order processing system right from receiving the order to up until the point the payment is made and an entry is logged in your accounting books.What is AR-Account Receivables cycle?
The cash collection cycle is the number of days it takes to collect accounts receivable. The measure is important for tracking the ability of a business to grant a reasonable amount of credit to worthy customers, as well as to collect receivables in a timely manner. Use Accounts receivable to track customer invoices and incoming payments.What is Sales Invoices?
A sales invoice is an accounting document that records a business transaction. ... Typically, a sales invoice will include a description of the service provided, the amount owed and the deadline for payment.The most basic purpose for a sales invoice is to keep a record of the sale. It provides a way to track the date a good was sold, how much money was paid and any outstanding debt. The invoice is an invaluable tool for accounting. It can also track which employees make sales and the items they sell.
You can create customer sales invoices that are based on sales orders or packing slips. You can also enter free text invoices that are not related to sales orders. You can receive payments by using several different payment types. These include bills of exchange, cash, checks, credit cards, and electronic payments. If your organization includes multiple legal entities, you can use centralized payments to record payments in a single legal entity on behalf of the other legal entities.
How Sales Invoice effects New GST Returns Filing System?
This document of Sales invoice is main input documents for GSTR1 or GST ANX-1 Report.There are 2 Parts in system: GST ANX-1 & ANX-2 for Proper Reporting of Supplies
Under GST ANX 1, all outward supplies, inward supplies under reverse charge, and imports made during a particular tax period will need to be reported by the registered taxpayers.
Under GST ANX 2, details related to all the inward supplies from registered persons, supplies received from an SEZ unit/developer, and imports made by registered taxpayers will be reported.
Once a particular supplier uploads the documents related to supply in GST ANX 1, the recipient can also easily view those supply documents in his GST ANX 2. The recipient would also have the facility to take any action against these documents by either accepting them or rejecting them or put them in pending state with action to be taken at a later date.
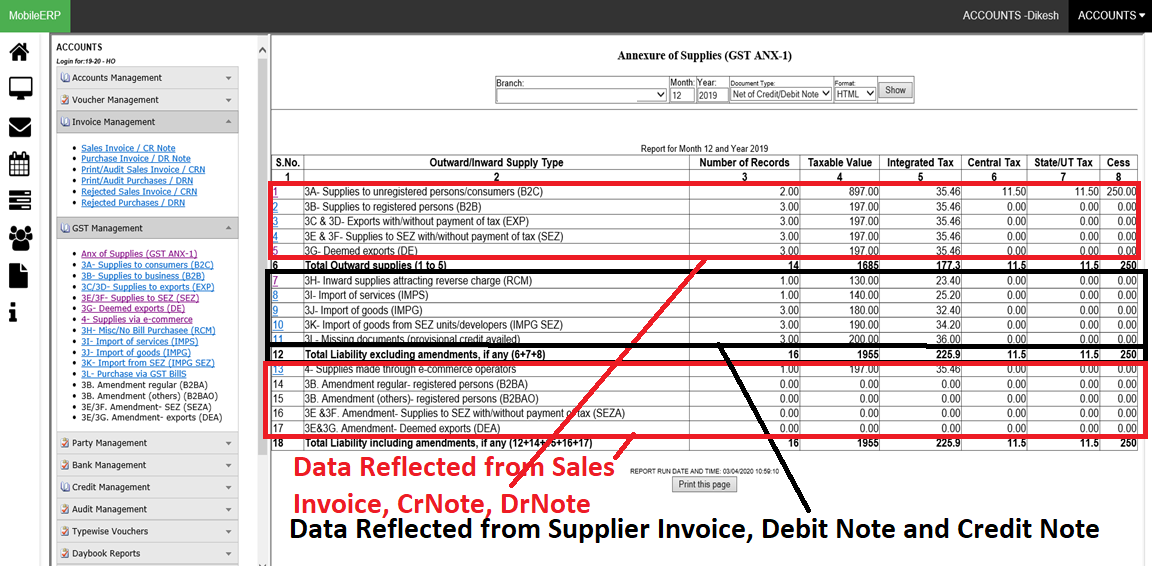
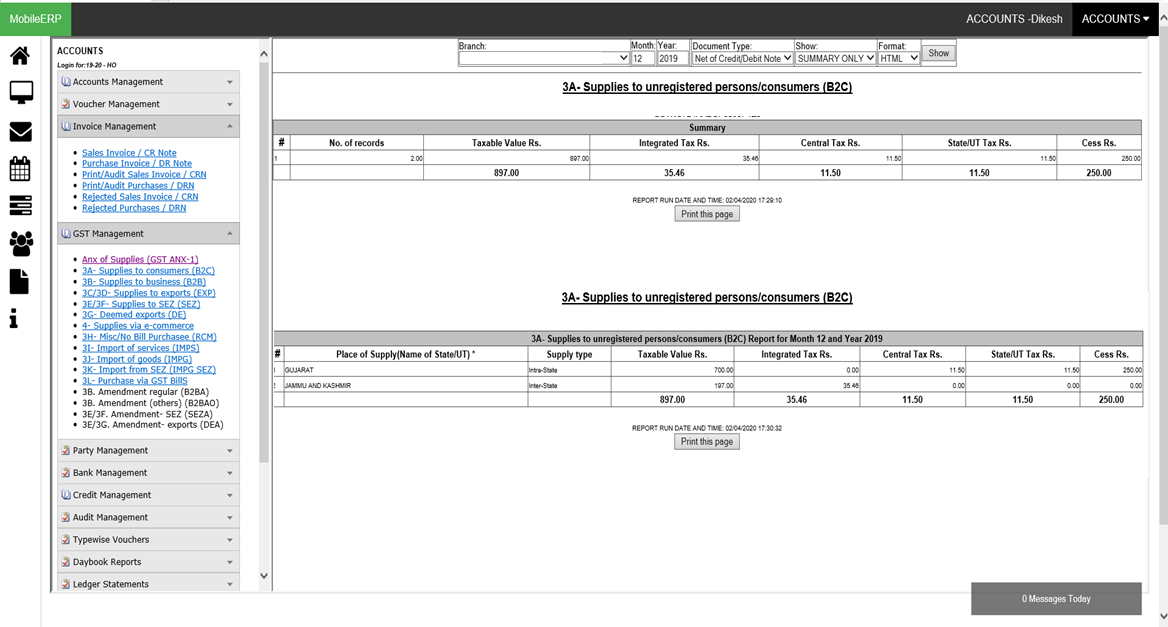
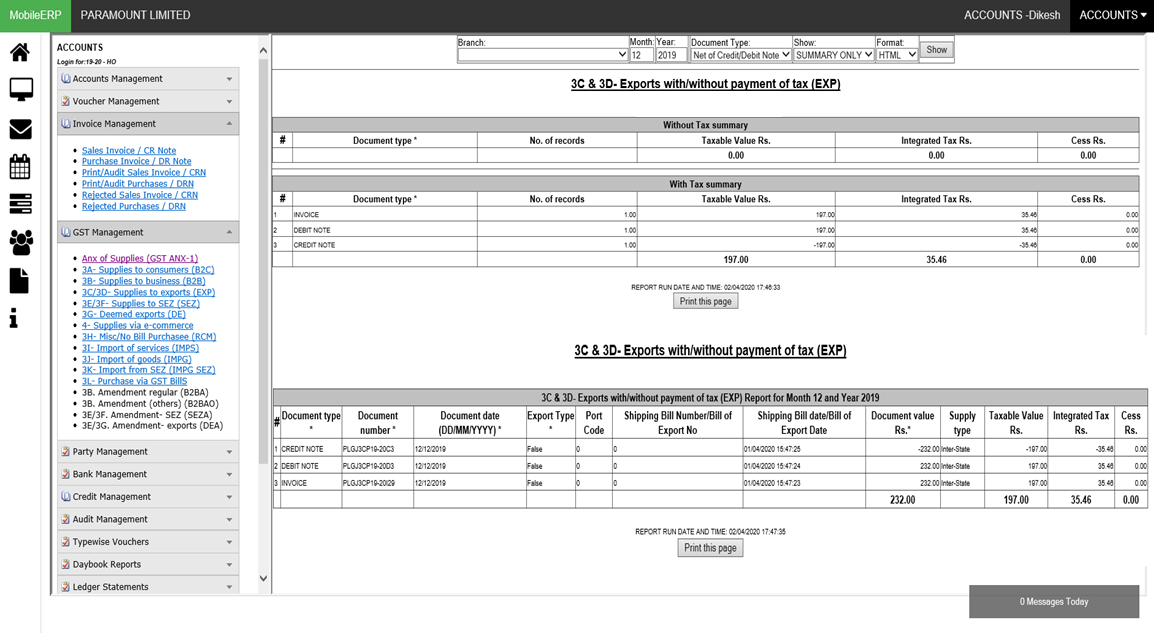
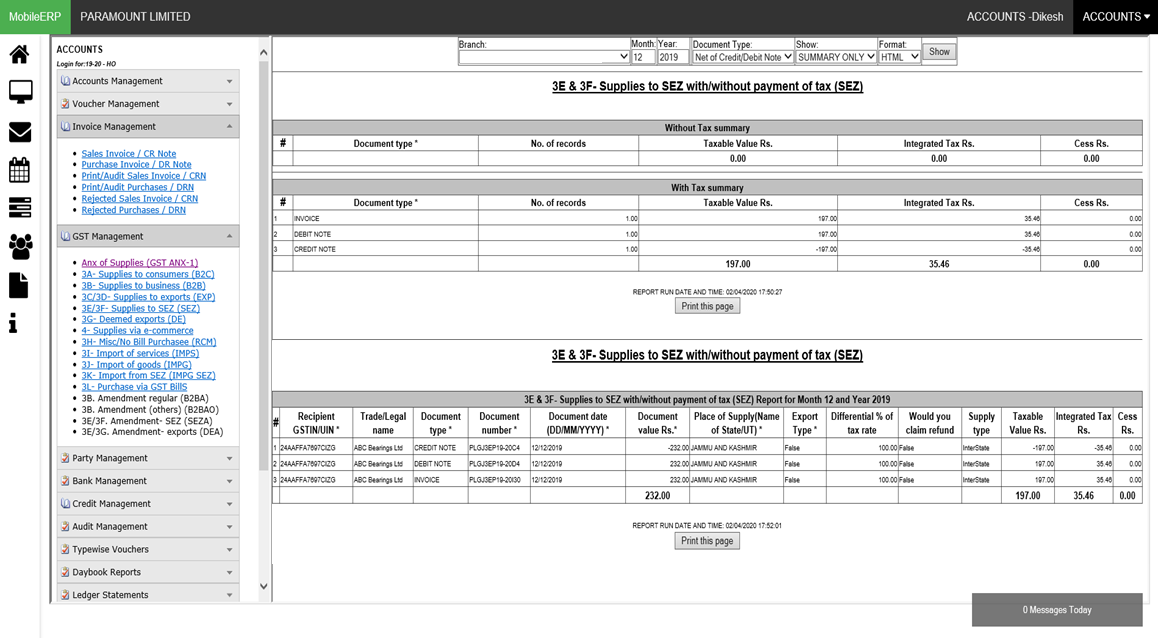
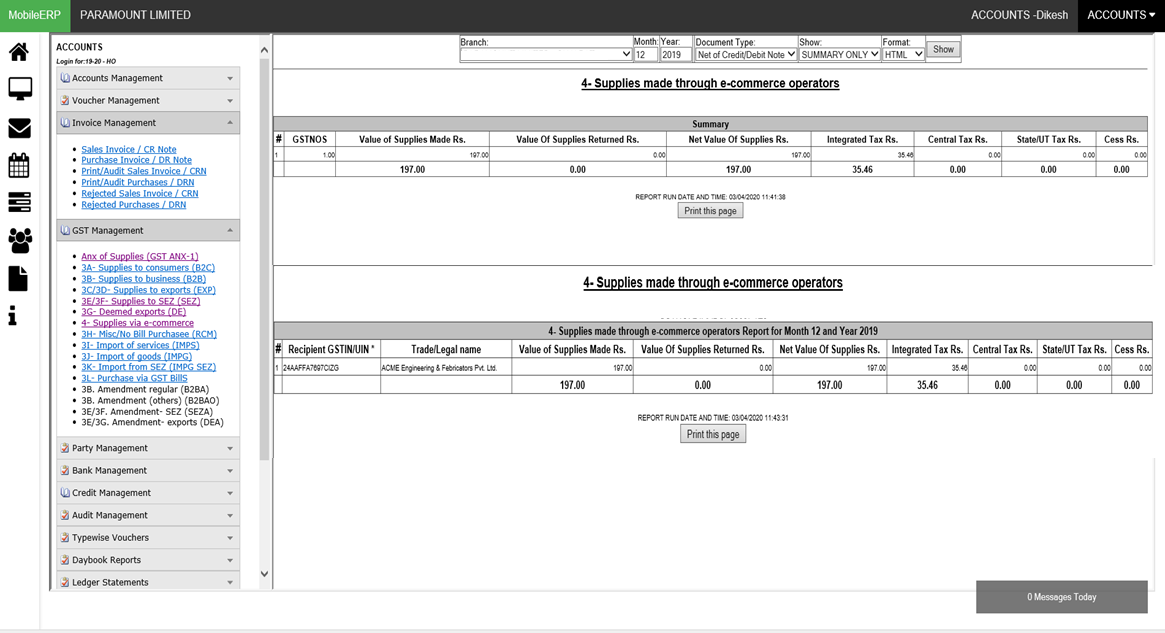
What are various types of Sales Invoices according to GST India
| 3A- Supplies to unregistered persons/consumers (B2C) | 3B- Supplies to registered persons (B2B) | 3C & 3D- Exports with/without payment of tax (EXP) | 3E & 3F- Supplies to SEZ with/without payment of tax (SEZ) | 3G- Deemed exports (DE) | 4- Supplies made through e-commerce operators |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
What Are the Different Types of Sales Invoices?
The different types of invoices that businesses can create for their clients are:1. STANDARD INVOICE
A standard invoice is issued by a business and submitted to a client. This is the most common form of invoice that small businesses create and the format is flexible enough to fit most industries and billing cycles. Standard invoices include the following details about the sale:
The business’s name and contact information, The client’s name and contact information, An invoice number, The amount of money the client owes the business for its services
2. CREDIT INVOICE OR CREDIT NOTE
A credit invoice, also called a credit memo, is issued by a business that needs to provide a client with a discount or a refund, or to correct a previous invoicing error. A credit invoice will always include a negative total number. For example, if you’re providing a credit invoice to a client to detail a $50 refund, the total on the credit invoice would be -$50.
3. DEBIT INVOICE OR DEBIT NOTE
A debit invoice, also called a debit memo, is issued by a business that needs to increase the amount a client owes to the business. Debit invoices can be useful to small businesses and freelancers when they need to make a slight adjustment to an existing bill. For example, if you sent a client an invoice based on your estimated hours and you ended up working additional hours on a project, you could send the client a debit invoice for the additional hours billed. Debit invoices are always written as positive numbers.
4. MIXED INVOICE
Mixed invoices combine credit and debit charges on one invoice, and the total amount can be expressed as either a positive or negative number. Small businesses rarely need to create mixed invoices for their services, but it could be necessary if you’re reducing the amount a client owes for one of the projects you’re billing for and increasing the amount owing for a different project billed on the same invoice.
5. COMMERCIAL OR EXPORT INVOICE
An export invoice is really an umbrella term that encompasses exporting forms like the Commercial Invoice and the Proforma Invoice—forms that indicate the buyer and seller of the goods, a description of the items, the items' value, and the terms or proposed terms of the sale. A commercial invoice is issued by a business for goods that it sells to customers internationally. Commercial invoices include details of the sale that are needed to determine customs duties for cross-border sales. The information included on a commercial invoice includes:
Shipment quantity, Weight / volume, Description of goods, Total value, Packaging format
6. TIMESHEET INVOICE
A timesheet is an invoice used when a business or employee is billing based on the hours they work and their standard rate of pay. Timesheets are used by contract employees who are paid hourly by their employer. They’re also common in industries where clients are billed hourly, including by:
Lawyers, Creative agencies, Business consultants, Psychologists, Programmers, IT Staff etc.
7. EXPENSE REPORT
An expense report is a type of invoice that an employee submits to an employer for reimbursement of business-related expenses. For instance, if you send an employee to a lunch meeting with a client, they can create an expense report to invoice your company for the cost of the lunch, parking and gas that they paid up front.
8. PRO FORMA INVOICE
A pro forma invoice is an estimated invoice that a business sends to a client before providing their services. A pro forma invoice provides the client with an estimated cost of the work to be completed. Pro forma invoices may have to be altered once a project is complete to accurately reflect the hours worked.
9. INTERIM INVOICE
An interim invoice is used for billing on large projects where the business and the client have agreed to terms that include multiple payments. A business or freelancer will submit interim invoices when certain milestones are completed toward the larger project. Interim invoices help small businesses manage their cash flow while working on projects over long periods of time.
10. FINAL INVOICE
A final invoice is sent to the client once a project has been completed to request payment. The final invoice is usually more detailed than a pro forma or interim invoice and typically includes the following:
An itemized list of all services provided, Total cost of the project, Invoice number, Invoice due date, Payment methods accepted etc.
11. PAST DUE INVOICE
A past due invoice is sent by a business if their client doesn’t provide payment by the due date listed on the final invoice. You should send past due invoices to clients as soon as they miss a payment due date. Past due invoices include all the service and payment details listed on the final invoice and they also include any late fees or interest charges.
12. RECURRING INVOICE
Recurring invoice are useful for businesses that charge clients the same amount periodically for their services. Recurring invoices are common among IT businesses, who charge their clients the same amount each month for a package IT service. Or, if you’re a freelance digital marketer, you might offer social media marketing packages to your clients with standard pricing per month. Cloud-based invoicing software lets you automate the process of creating recurring invoices and can even send out the invoices on the same day each month, so you don’t have to think about it. e.g. Utility bills like GAS, Electricity etc.
13. SUBSCRIPTION INVOICE
We are no longer selling products or services, but rather we are selling offer-ings. That tends to be more of a usage and subscription based model rather than a one-off bump in revenues. Moving from product to a subscription service leveraging usage-based pricing models as opposed to a traditional product approach is major challenge for SMEs. For B2B-oriented companies, the shift from selling products to offering subscription services has a dramatic impact on how business is booked and revenue is recognized. It is not the spike that happens toward the tail-end of the quarter as products are shipped. The revenue stream is normally lower (at least initially) but more constant and predictable (i.e., there is more predictability from a three-year subscription than from the spikes linked to product sales). This changes how the business is managed, and how financial investors value the company. e.g. Cars sold on lease and buy back offers, Amazone Prime or Netflix Subscriptions, Tata Sky or Jio Subscriptions etc.
14. E-INVOICE
E-invoice is a blanket term applied to any invoice sent electronically, regardless of the specific type of invoice being sent. E-invoicing is becoming standard practice among small businesses and freelancers. E-invoices are quicker and easier to create than standard print invoices and they help you get paid faster for your services.
15. REAL ESTATE INVOICE OR PAYMENT RECEIPTS
Real estate invoices are used by agents, brokers and realtors to collect commissions on the sale of residential and commercial properties. Real estate invoices offer information specific to the industry, including details about the property sold, the sale price and the agent’s commission rate.
Real estate invoices help agents get paid for their sales commissions. They also record important accounting information. Invoices help agents track their home sales, compare their year-over-year commission revenue and provide important insights about the financial health of the business.
Maintaining soft copies of key documents like sale contracts and deed forms is a smart practice in the real estate business. With MobileERP Invoice, you can get smarter by attaching those documents directly to your invoices when you close a deal.
16. RETAIL INVOICE OR B2C - BUSINESS TO CONSUMER INVOICE
A retail invoice is an invoice issued by the seller to the buyer for the amount due against the goods sold to him.
17. TAX INVOICE OR B2B - BUSINESS TO BUSINESS INVOICE
A tax invoice is an invoice issued by a registered dealer to the registered purchaser, showing the amount of tax payable. Tax invoices are also needed to claim tax credits
18. CASH MEMO OR CASH RECEIPTS
A cash memo is prepared when goods are sold for cash. Thus, a cash memo is given by a trader in the case of sale and it is received in the case of purchases. Cash memos are used for cash purchases/sales in order to record the credit purchases/sales, an invoice or bills are prepared by the seller. Cash Memo is a source document used in case of a cash transaction between the seller and a buyer. In case of a cash sale, the seller prepares the cash memo and hands it over to the purchaser. It acts as a proof for all cash sales made by a business.
An Invoice is raised before the payment while cash memo is raised when the payment is made. An Invoice is issued for the credit transaction as a proof of amount due, whereas cash memo is issued for cash transaction as a proof of the amount received. ... On the other hand signature of cashier is found in the cash memo.
Cash Memo and Cash Receipt are used to acknowledge the receipt of cash. Cash Memo is also a non-negotiable commercial instrument indicating, ... However, Cash receipt is an acknowledgement of cash received. Cash Receipts are given for commercial and non-commercial transactions. e.g. College Fee Receipts, POS Super Market Bill cum receipts on thermal paper etc.
19. CHALLAN OR E-CHALLAN
Challan is an official form or other kind of document, piece of paperwork, citation, etc. ... E-challan is an electronic format of the challan. An e-challan can also be defined as a specific format used for depositing or remitting the contribution or statutory payment at a bank or treasury. All payments of taxes in India is done via Challan. Instead of Invoice, a payment challan is raised by Government to collect the taxes from companies.
20. RA BILL OR RUNNING ACCOUNT BILL
Running Account Bill means a bill for the payment to be made to the Contractor on a running account when payment for work is made to him at specified intervals, subject to deductions as per contract and final settlement of the account on completion or determination of his contract. RA Bills are prepared as per Measurement Book for each period. Measurement Book is record book in which transaction details of work done of contract is enetred and maintained. Measurement Book is attached to RA Bill as proof of work.
21. FREE TEXT OR SERVICE INVOICE
A free text invoice is an invoice that is not attached to a sales order and does not require a sales order or packing slip. Free text invoices are used to sell a quantity of any kind of goods or services that are not in your inventory. e.g. Rent Bills, Service Bills, Maintenance Bills, Field Service bills, Jobwork invoice etc.
22. CONSIGNMENT SALES INVOICE OR E-COMMERCE SALES INVOICE
A consignment invoice is the document that a consignor delivers to a consignee when payment for consigned goods becomes due. Advantages of consignment selling is : It allows a seller (manufacturer) to place merchandise in wholesale and retail outlets for additional exposure to the buying market. It can provide an incentive for the wholesaler and retailer to stock goods in inventory because their capital is not tied up in inventory. Ownership of goods lies with seller till it is sold. e.g. mall outlet stores, ecommerce invoice etc.
23. RETAIL POS INVOICE OR B2C RETAIL SALES
The point of sale (POS) or point of purchase (POP) is the time and place where a retail transaction is completed. At the point of sale, the merchant calculates the amount owed by the customer, indicates that amount, may prepare an invoice for the customer (which may be a cash register printout), and indicates the options for the customer to make payment. It is also the point at which a customer makes a payment to the merchant in exchange for goods or after provision of a service. After receiving payment, the merchant may issue a receipt for the transaction, which is usually printed but can also be dispensed with or sent electronically.
To calculate the amount owed by a customer, the merchant may use various devices such as weighing scales, barcode scanners, and cash registers. To make a payment, payment terminals, touch screens, and other hardware and software options are available with MobileERP.
The point of sale is often referred to as the point of service because it is not just a point of sale but also a point of return or customer order. POS terminal software also include features for additional functionality, such as inventory management, CRM, financials, or warehousing ETC. Businesses are increasingly adopting POS systems, and one of the most obvious and compelling reasons is that a POS system does away with the need for price tags. Selling prices are linked to the product code of an item when adding stock, so the cashier merely needs to scan this code to process a sale. If there is a price change, this can also be easily done through the inventory window. Other advantages include the ability to implement various types of discounts, a loyalty scheme for customers, and more efficient stock control, and these features are typical of almost all modern ePOS systems.
Only one combined invoice for days sales per store are posted into company accounts. All GST Taxes are clubbed into single invoice per day per store for reporting purpose.
24. AMC/CMC/WARRANTY EXTENION CONTRACT INVOICE:
AMC stands for Annual Maintenance Contract. ... Generally, this type of contracts is signed for one year at a time. It can be extended up to two or more years as per the agreement between the parties. In AMC, the company usually provides service support to the customer and charges for the faulty parts of the machine.
CMC stands for Comprehensive Maintenance Contract. ... Generally, this type of contracts is signed for one year at a time. It can be extended up to two or more years as per the agreement between the parties. In CMC, the company usually provides service support to the customer and do not charges for the faulty parts of the machine.
An extended warranty, sometimes called a service agreement, a service contract, or a maintenance agreement, is a prolonged warranty offered to consumers in addition to the standard warranty on new items. The extended warranty may be offered by the warranty administrator, the retailer or the manufacturer.
25. BRANCH TRANSFER OR STOCK TRANSFER OR GODOWN TRANSFER
Though stock transfers are taxable under GST, the tax is fully allowed as credit. This will eradicate the cascading effect which exists under current regime and as a result, products will be more cost effective. As per the rules laid down with respect to Eway bill, a manufacturer (supplier) is required to generate the Eway bill for stock transfer or branch transfer if the value of such consignment exceeds INR 50,000.
26. REPLENISHMENT INVOICE
This is the process of reordering items that you have previously purchased in order to meet demand. For example, let’s say that you ordered 100 t-shirts, but now you are low on stock. Instead of creating a new order from scratch, you will “replenish” your current stock levels by reordering more t-shirts. This process moves inventory between facilities or between suppliers to meet your consumer demand.
Replenishment should occur when your products reach their reorder point. This is so that you can avoid stock shortages from occurring. In an inventory management system, it can calculate the reorder point based on the parameters you set for each item. For example, the min, max, lead times, and safety stock.
An Invoice and e-Way Bill needs to be repared when goods are transfered from Warehouse to Retail Stores.
27. FULFILLMENT INVOICE OR WHOLESALE INVOICE
Fulfillment is what takes a product from the supplier to their customer. This includes, but is not limited to: receiving, processing, delivery, and returns of the product. Often unique to each firm, these processess can vary in complexity. Replenishment focuses on the quantity of inventory being restocked, whereas fulfillment deals with the processes involved in completing an order.
You may think that fulfillment is a very simple process. But depending on your operations, it can become very complicated. That’s why it is vital to use an inventory management system that can cater to your needs. This will provide you with greater accuracy and visibility into your inventory processes.
An Wholesale Invoice needs to be prepared in case of direct fulfillment. This Invoice can be Tax or Retail based on customer. It can also have e-way bill or direct hand-to-hand delivery.
28. EWAY BILL
EWay Bill is an Electronic Way bill for movement of goods to be generated on the eWay Bill Portal. A GST registered person cannot transport goods in a vehicle whose value exceeds Rs. 50,000 (Single Invoice/bill/delivery challan) without an e-way bill that is generated on ewaybillgst.gov.in.
Alternatively, Eway bill can also be generated or cancelled through SMS, Android App and by site-to-site integration through API.
When an eway bill is generated, a unique Eway Bill Number (EBN) is allocated and is available to the supplier, recipient, and the transporter.
When Should eWay Bill be issued? eWay bill will be generated when there is a movement of goods in a vehicle/ conveyance of value more than Rs. 50,000 (either each Invoice or in aggregate of all invoices in a vehicle/conveyance) –
-In relation to a ‘supply’
-For reasons other than a ‘supply’ ( say a return)
-Due to inward ‘supply’ from an unregistered person
For this purpose, a supply may be either of the following:
-A supply made for a consideration (payment) in the course of business
-A supply made for a consideration (payment) which may not be in the course of business
-A supply without consideration (without payment)In simpler terms, the term ‘supply’ usually means a:
For Transaction like:
1. Sale – sale of goods and payment made
2. Transfer – branch transfers for instance
3. Barter/Exchange – where the payment is by goods instead of in money
Therefore, eWay Bills must be generated on the common portal for all these types of movements. For certain specified Goods, the eway bill needs to be generated mandatorily even if the value of the consignment of Goods is less than Rs. 50,000:
1. Inter-State movement of Goods by the Principal to the Job-worker by Principal/ registered Job-worker,
2. Inter-State Transport of Handicraft goods by a dealer exempted from GST registration
Documents or Details required to generate eWay Bill
Invoice/ Bill of Supply/ Challan related to the consignment of goods
Transport by road – Transporter ID or Vehicle number
Transport by rail, air, or ship – Transporter ID, Transport document number, and date on the document
Who should Generate an eWay Bill?
a. Registered Person – Eway bill must be generated when there is a movement of goods of more than Rs 50,000 in value to or from a registered person. A Registered person or the transporter may choose to generate and carry eway bill even if the value of goods is less than Rs 50,000.
b. Unregistered Persons – Unregistered persons are also required to generate e-Way Bill. However, where a supply is made by an unregistered person to a registered person, the receiver will have to ensure all the compliances are met as if they were the supplier.
c. Transporter – Transporters carrying goods by road, air, rail, etc. also need to generate e-Way Bill if the supplier has not generated an e-Way Bill.
Validity of eway bill is normally 1 days for every 100 km or 20 km based on size of cargo.
How to do Sales Accounting