Implementing Industry 4.0 is a strategic priority for your manufacturing company
Fast-track time to market, gain new production efficiencies, and lower costs with manufacturing software and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions.
Repetitive
Electronic goods, Cars, Durable goods, Textile yarns, Medical Instruments, Subcon Parts
Discrete
Furniture, Toys, Smartphones, Airplanes, Machinery, Metal Parts, Readymade Clothes
Jobshop
Machine tool shop, Paint shops, French restaurant, Tools, Die, Computers, Tailored Clothes, EPC Building or Factory
Process
Food, Beverages, Refined oil, Gasoline, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals, Plastics, Oxygen Cylinders



Implementation work for MRP Managers
TEAM
SuppliersTOStores
StoresTOFloor/Subcons
FloorTOStores/Scrap
SubconTOFloor
FloorTOWarehouse
WarehoueTOCustomers
TARGETS
Increase Labour Productivity
Increase Manpower Utilization
Reduce Manpower related costs
Enhances inventory management,
Minimising waste, rework, rejects
Make vs Buy Strategy optimization
GOALS
Reduction in scrap costs
Reduction in rework costs
Reduction in obsolence costs
Increase Machine Utilization
Increase Plant Utilization
Reduce Production Delays/costs
ACTIONS
M2O/M2S-MRP
Manufacturing Order
Shopfloor Routing
Machine Loading
Production Log
Machine Log
Simplify
1. Forecasting
2. Production
3. Floor Space Utilization
4. OEE Monitoring
5. Routing
Automate
1. Forecasting
2. Production Scheduling
3. Breakdown Detection
4. Industry 4.0 IOT
5. Material Planning
Control
1. Production Costs
2. Energy Costs
3. Manpower Costs
4. Accidents
5. Quality
Eliminate
1. Process bottlenecks
2. Rework/Repetitive Work
3. Delays in Production
4. Quick Change Overs
5. Scrap/Obsolence
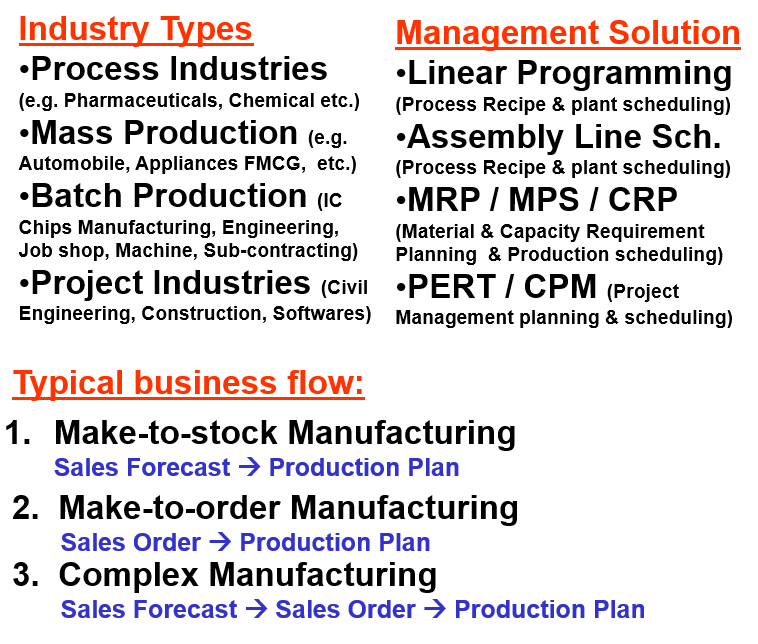
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the use of labor, machines and tools to make goods for sale or use. You need MobileERP Software Visual Board as follows on Shopfloor with big TV Screen to manage proper production.
What are different types of Manufacturing?
Most manufacturing environments fit into one of five general categories. Repetitive, Discrete, Job Shop, Process (batch), and Process (continuous). Most companies use more than one of these environments to get a single product out the door.
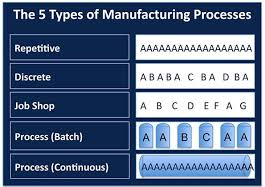
Examples of Manufacturing Industries:
Oil&Gas> Textiles> FMCG-WhiteGoods> Packaging
What is Repetitive Manufacturing?
Repetitive manufacturing (REM) is the production of goods in rapid succession. Goods that are created through repetitive manufacturing follow the same production sequences. Repetitive manufacturing often goes hand-in-hand with automated assembly processes.
Since you're manufacturing products ahead of a customer's order, the process needs a master production schedule to run efficiently. Businesses that utilize repetitive manufacturing are ones who, for example, produce electronic goods, cars, and durable goods.
What is Discrete Manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing is the manufacturing of individual finished products, that can be counted, touched, and seen.
Discrete Manufacturing Process Flows are
— Make-to-stock (MTS);
— Make-to-order (MTO); and.
— Assembly-to-order (ATO).
Automobiles, furniture, toys, smartphones, and airplanes are examples of discrete manufacturing products. The resulting products are easily identifiable and differ greatly from process manufacturing where the products are undifferentiated, for example oil, natural gas and salt.
Discrete Manufacturing Vs Repetitive Manufacturing Difference.
Typical of order-based production is the frequent switching from one product to another. Each product is manufactured in individually defined lots. ... In repetitive manufacturing, the same product is produced on a certain production line over a longer period of time.
The ERP system for discrete manufacturers needs to keep track of parts, whether they are things like nuts and bolts, or completed engine assemblies.
Typical challenges for discrete manufacturers include the following:
Balancing inventory investment with customer service levels
Controlling product design changes (for batch manufacturers)
Ensuring the quality of parts and raw materials
Identifying and responding to seasonal demand patterns
Managing component requirements
Reducing lead times
Reducing forecast errors
Synchronizing supply with customer demand

What is Jobshop Manufacturing?
A job shop is a type of manufacturing process in which small batches of a variety of custom products are made. In the job shop process flow, most of the products produced require a unique set-up and sequencing of process steps.
Job shops are usually businesses that perform custom parts manufacturing for other businesses. However, examples of job shops include a wide range of businesses—a machine tool shop, a machining center, a paint shop, a commercial printing shop, and other manufacturers that make custom products in small lot sizes.
Job production is where a single product is made at a time. ... Job production tends to be labour intensive, and often highly skilled labour is required. Examples include building ships, bridges and buildings, handmade crafts like furniture and made-to-measure clothes.
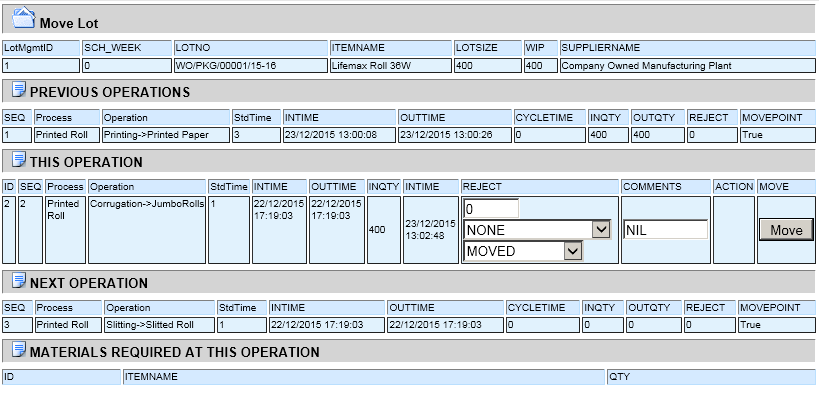
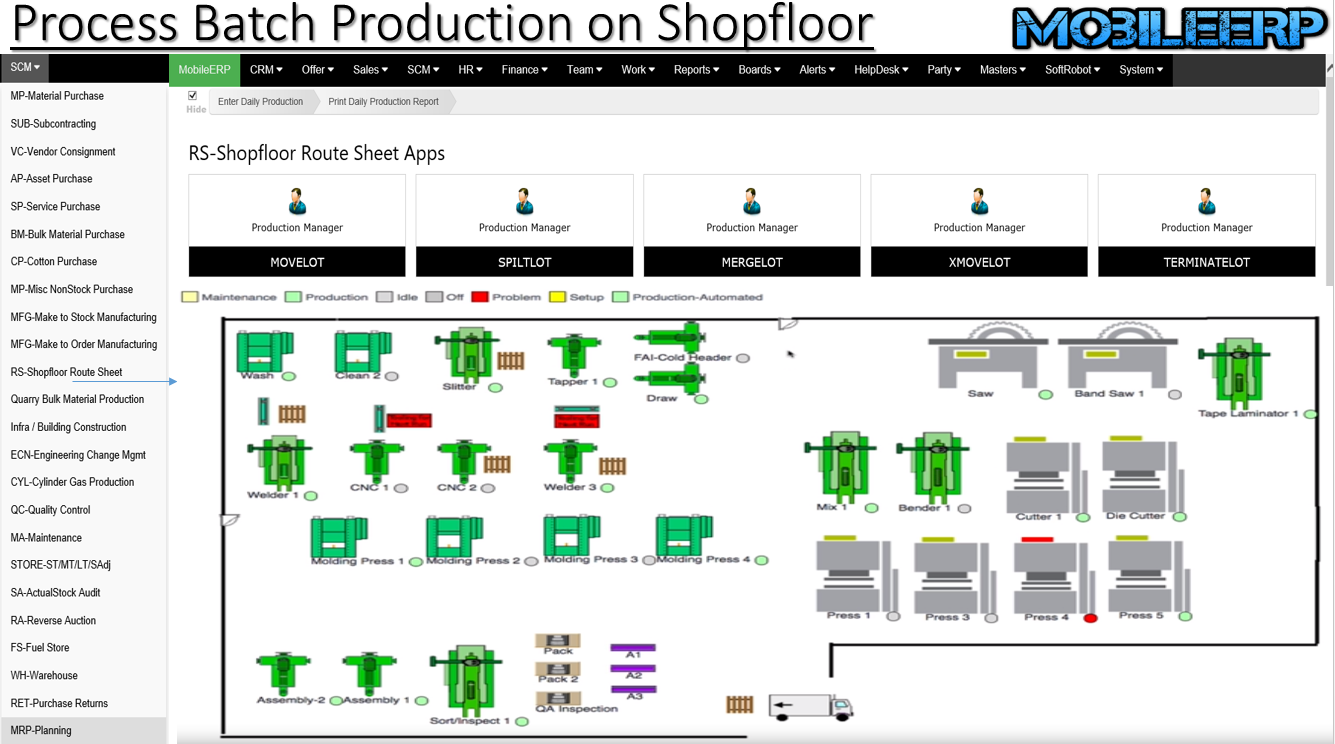
What is Batch Process Manufacturing?
Process manufacturing is a production method that creates goods by combining supplies, ingredients or raw materials using a formula or recipe. It is frequently used in industries that produce bulk quantities of goods, such as food, beverages, refined oil, gasoline, pharmaceuticals, chemicals and plastics.
Batch manufacturing is a style of manufacturing which compiles the different components of a product through step by step processes. This basically means that the raw materials move through the production line in batches, so that there is a pause between each step as a batch moves through.
Job shop is based typically on flexible resources which can produce very different product variants. ... In batch production products are produced in batches. A product is produced more than once, but not continuously. The production can be organized for example in production cells or into flow production.

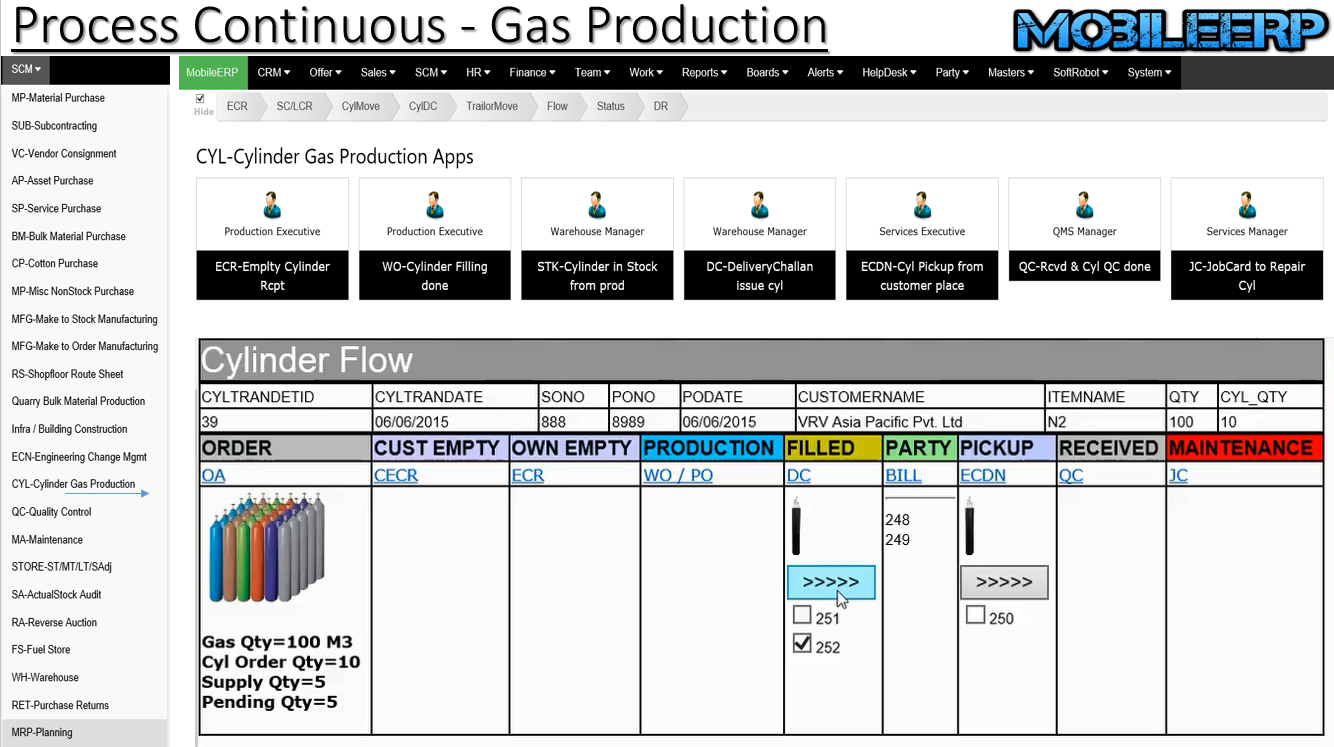
What is Continues Process Manufacturing?
A continuous process, on the other hand, refers to a processing that involves moving a single work unit at a time between every step of the process without any breaks in time, substance, sequence or extend. As the name suggests, the flow of product or material is continuous. Every machine operates in a steady state and performs a certain processing function.
For majority of applications, continuous flow saves costs, energy and time. When this process is properly implemented, it can reduce waste, improve quality by making it easier to identify and correct errors, increase productivity and adapt to the needs of customers more efficiently than batch processing.
The ERP system for process manufacturers needs to keep track of ingredients. This means you need to track weights, volumes and, in many cases, expiry dates.
Typical challenges for process manufacturers include the following:
Accommodating variable end-products which result from regarding and unpredictable chemical processes
Controlling product formula changes
Monitoring the quality of raw materials before and during production
Managing complex production recipes
Managing different units of measure for raw materials and recipes
Tracing products and raw materials


What is Waste Recycle Manufacturing?
Currently, 90% of our waste is dumped in landfills, which is a major challenge to overcome requiring a massive mindset shift. However, with the upside of global warming as a spin-off, we should be compelled to adopt this system of Waste Recycle based Manufacturing as quickly as possible.
For example, plastics manufacturers will face the challenge of identifying and reporting on how much-recycled content is used in each packaging unit they sell. ERP allows for multiple inputs into the production process (both recycled and new resins) and keeps track of all raw material that makes up a finished item which is shipped to the customer. As a result, packaging manufacturers can easily trace and report on the percentage of recycled raw material that makes up the final item that is sold.
Manufacturers will also be looking to innovate and develop new products that will allow them to incorporate recycled material into their production processes without compromising on quality, tensile strength, the aesthetic look of the final product (recycled colored plastic ends up grey which marketers are reluctant to use), cost and so on. It’s clear that managing new product development while continuing production will be important. Again, ERP can support this need with strong Bill of Materials functionality.
What is Automated Smart Manufacturing Factory?
The smart factory is a flexible system that can self-optimize performance across a broader network, self-adapt to and learn from new conditions in real or near-real time, and autonomously run entire production processes.Many companies are making investments in smart factory capabilities to mitigate the risk associated with a possible labor shortage.
Example process:
eCommerce Order by Customer >>> Product Manufactured at Fully Automated Smart Manufacturing Factory as per Industry 4.0 >> Products Picked by Flying Drones and delivered to Customers.

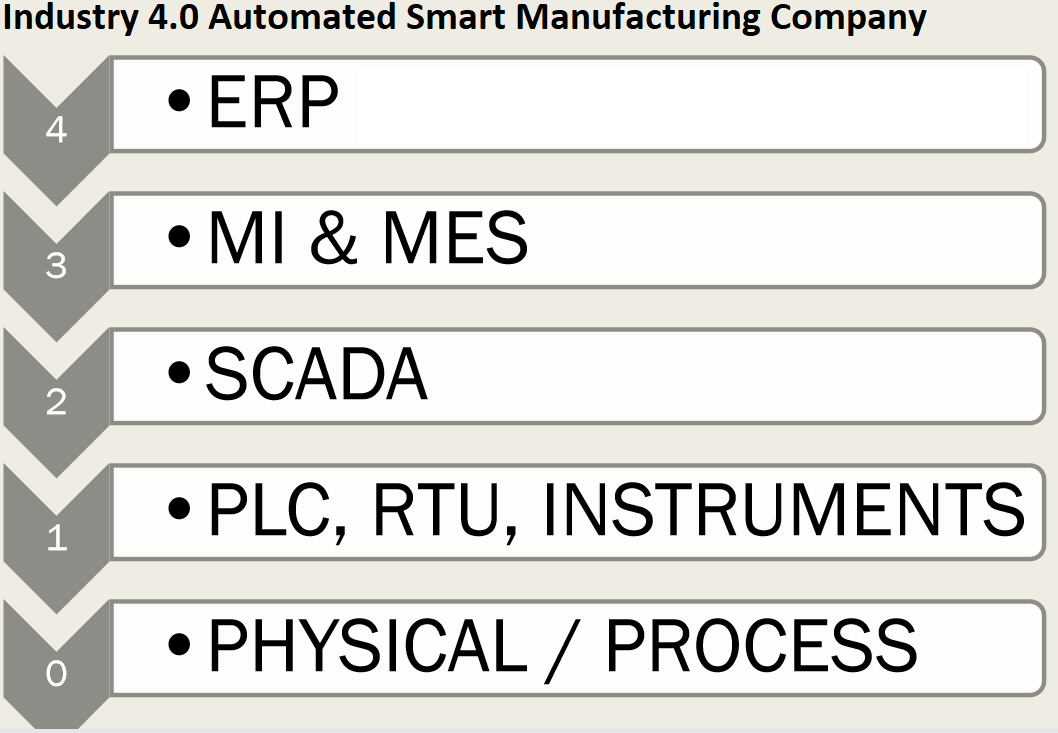
What is MRP2-Manufacturing Resource Planning?
Manufacturing Resource planning is a coordinated process involving demand management, forecasting, master scheduling, material requirement planning (MRP1), and capacity planning, fully integrated with operational management applications including production control, inventory management, and procurement.