Plan
Create New Campaigns
Do
Execute Campaigns
Check
Measure Campaign Effectiveness
Act
Improve Campaigns






CRM Implementation work for Marketing Managers
TEAM
Territorry
Marketing Network
Marketing Manager
Sales Executives
TARGETS
Contacts
Customers
Accounts
Competitors
GOALS
Budget
Campaign
Sales Targets
Collection Targets
ACTIONS
Campaign Execution
Product Mix Management
Pricelist Management
Scheme Management
Role: Salesmen1 / Year:2020 / Territorry: Assam
QUARTER1
Target: $42M
Budget: $5M
Campaign: $1M
Expenses: $1M
Balance Budget: $3M
Opportunity: $20M
LeadPipeline: $10M
Offers: $5M
Orders: $2M
Achievement: $2M
Collections: $1M
Incentive: $1k
QUARTER2
Target: $42M
Budget: $5M
Campaign: $1M
Expenses: $1M
Balance Budget: $3M
Opportunity: $29M
LeadPipeline: $11M
Offers: $5M
Orders: $2M
Achievement: $2M
Collections: $1M
Incentive: $1k
QUARTER3
Target: $42M
Budget: $5M
Campaign: $1M
Expenses: $1M
Balance Budget: $3M
Opportunity: $28M
LeadPipeline: $12M
Offers: $5M
Orders: $2M
Achievement: $2M
Collections: $1M
Incentive: $1k
QUARTER4
Target: $42M
Budget: $5M
Campaign: $1M
Expenses: $1M
Balance Budget: $3M
Opportunity: $22M
LeadPipeline: $14M
Offers: $5M
Orders: $2M
Achievement: $2M
Collections: $1M
Incentive: $1k
Simplify
1. Employee Work
2. Document Management
3. Management Reporting
4. Data Entry
5. Followups
Automate
1. Campaigns & Correspondance
2. Opportunity Generation
3. Lead Generation
4. Offer Preparation
5. Order Entry
Control
1. Costs
2. Employees
3. Collections
4. Process
5. Expenses
Eliminate
1. Duplicate Work
2. Rework
3. Repetitive Work
4. Travelling
5. Couriers
Understand the basics
What is CRM - Customer Relationship Management?
Customer relationship management is an approach to managing a company's interaction with current and potential customers. It uses data analysis about customers' history with a company to improve business relationships with customers, specifically focusing on customer retention and ultimately driving sales growth.
Let's take a look at the role CRM plays in customer-centricity, customer data management and automation.
1. Supports a customer-centric strategy
A CRM system supports a strategy which says that the customer is at the center of everything that you do. This customer-centric strategy must be based on clear goals and a vision of what a meaningful customer experience looks like.
A valuable customer experience is an integral part of CRM, according to Gartner’s report, “Improving the Customer Experience”.
Every time a customer comes in contact with an organization, through any of its channels, the customer has an opportunity to form an opinion – be it good, bad or indifferent. Through time, this collective set of customer experiences forms a picture in the customer’s mind, which in turn, forms the image of the brand its values.
Organizations that are serious about CRM design and maintain a quality customer experience because they recognize that a poor customer experience is a step toward customer churn, whereas a good experience encourages loyalty.
2. Centralizes all your customer data
CRM software combines all sales, marketing and customer service information into one central database.
With 92% of businesses collecting data on prospects and customers, having access to all data in database means fewer silos within your organization - thus helping you achieve customer centricity.
3. Automates customer-facing business processes
Companies have business-facing processes and customer-facing processes.
Business-facing processes are those which make the business run more efficiently such as budgeting and planning whereas customer-facing processes include sales, marketing and customer service.
A CRM strategy focuses primarily on the customer-facing processes and makes them better in terms of meeting the needs of the customer.
The following chart explains a sample what is included in each process:
Software Components of CRM:

CRM : MARKETING / SALES-Salesperson Portal / Offer/ Tender / Customer Service Management / Budgets and Expenses
What are types of CRM - Customer Relationship Management?
CRM can analyze data and generate reports whenever required. There are mainly three types of CRM applications – Operational, Analytical and Collaborative to perform all these activities.
What is difference between ERP and CRM?
ERP stands for “Enterprise Resource Planning.” ERP is designed to improve the efficiency of your business processes to reduce overhead and cut costs. But while CRM focuses on prospect and customer interactions, ERP focuses on all aspects of your business.
What are various components of CRM - Understand the difference between leads, opportunities, accounts, and contacts?.
1. Accounts represent companies that your organization does business with or are customers and will have sundry debtors account.
2. Contacts are people who represent an account. Prospects who could be potential customers also are Contacts. All customers are contacts, but all contacts are not customers.
3. Leads are potential or prospective customers. Leads are recorded and followp done so that an offer can be made by raising customer interest or customer relation and trust.
4. Opportunities are not a specific customer, such as a lead, contact, or account, and therefore require a customer record to be added to the opportunity.
5. Customers can be accounts, contacts, or leads. You can also use relationship roles to define how specific account, opportunity, and contact records are be related to one another in CRM.
Why CRM is important for your business?
CRM is more important than ever to businesses because it can help you to gain new customers and retain existing ones.
In today’s highly competitive environment and with so many products and services to choose from, customers are picky and customer loyalty seems to be a thing of the past.
The moment a new product is introduced into the market, it takes only a few months before that product or service suddenly becomes a commodity, which, in turn, means it’s easy to switch companies.
And despite what you might think, not all customers are created equal.
Some are a drain on customer service teams despite spending very little. Other customers do business frequently, often buy new products and services and may even be strong influencers in their market.
In cases like these, CRM helps prioritize sales and marketing efforts when dealing with different customer groups.
It also gives companies a better way of understanding customer needs and wants in order to improve the way the product portfolio is offered to them. The more you know about your customers, their buying preferences and behavior, the more likely your offer will be on target.
Marketing Automation
What is Marketing Automation?
 Marketing automation refers to software platforms and technologies designed for marketing departments and organizations to more effectively market on multiple channels online and automate repetitive tasks.
Marketing automation refers to software platforms and technologies designed for marketing departments and organizations to more effectively market on multiple channels online and automate repetitive tasks.
Marketing Mix Setup-Products, Pricelist and Scheme Automation
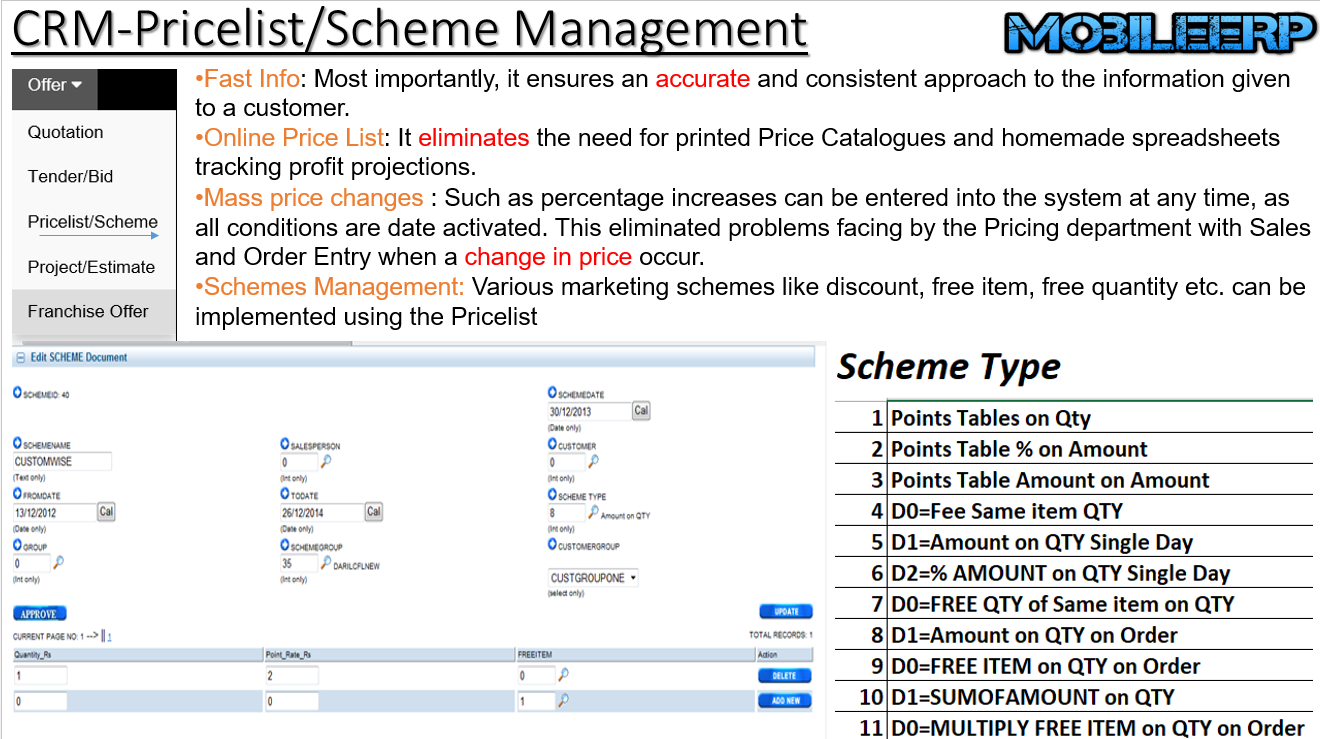
What is Pricelist or Scheme Strategy?
The marketing mix is a very important concept of marketing which involves the 4 main elements i.e people, promotion, place and price. However, the second most important factor in the marketing mix after product is the type of pricing being used. This is because the type of pricing can alter the distribution and the promotion mix as well.
When establishing a new company or even after years of existence on the market, it is a big challenge to set up the right price for your products and services. The dilemma is, if you set the price too high you risk losing customers or not attracting customers at all, and if you set it too low, you will probably have no return on your investment and very low margins.
There are several factors which need be taken into consideration before setting up prices, and these factors are influenced by current market supply and demand, competition levels as well as other political and economic influences. During the price planning process, your main focus should lie in finding the right price point where you can maximize your sales and profits. This usually depends on your individual marketing goals and objectives.
11 different types of pricing strategy should be implemented by Marketing Manager based on product and market conditions.
1) Premium pricing e.g. Audi, BMW, Merc etc. pricing
2) Penetration pricing e.g. Reliance Jio 4G/5G etc.
3) Economy pricing e.g. Walmart type pricing
4) Skimming price e.g. Apple iphone, Samsung Note etc. with competitive advantage
5) Psychological pricing e.g. $4,99 than products costing $5 as sold by super markets
6) Neutral strategy e.g. Rarely used, keeping the same price for life cycle of product.
7) Captive product pricing For example, the ink for a printer is a captive product sold at higher price, where the core product is the printer sold at low price.
8) Optional product pricing e.g. Food purchase in AirAsia Airlines.
9) Bundling price:e.g. Ever hear of the offer of 1 + 1 free? Free Shaving cream with Razor. Used to get rid of excess stock.
10) Promotional pricing strategy: e.g. Promote new product for limited period low pricing.
11) Geographical pricing: e.g. variations of prices depending on the location, taxes and transport cost
What is Transfer Pricing?
Transfer pricing can be defined as the value which is attached to the goods or services transferred between related parties. In other words, transfer pricing is the price which is paid for goods or services transferred from one unit of an organization to its other units situated in different countries (with exceptions).What are Transactions subject to Transfer pricing
The following are some of the typical international transactions which are governed by the transfer pricing rules:Sale of finished goods;
Purchase of raw material;
Purchase of fixed assets;
Sale or purchase of machinery etc.
Sale or purchase of Intangibles.
Reimbursement of expenses paid/received;
IT Enabled services;
Support services;
Software Development services;
Technical Service fees;
Management fees;
Royalty fee;
Corporate Guarantee fees;
Loan received or paid.
Purposes of Transfer Pricing
The key objectives behind having transfer pricing are:
Generating separate profit for each of the divisions and enabling performance evaluation of each division separately.
Transfer prices would affect not just the reported profits of every center, but would also affect the allocation of a company’s resources (Cost incurred by one centre will be considered as the resources utilized by them).
The profitability of a subsidiary depends on prices at which the inter-company transactions occur. These days the inter-company transactions are facing increased scrutiny by the governments. Here, when transfer pricing is applied, it could impact shareholders wealth as this influences company’s taxable income and its after-tax, free cash flow.
It is important that a business having cross-border intercompany transactions should understand transfer pricing concept, particularly for the compliance requirements as per law and to eliminate the risks of non-compliance.
Sales Organization Setup

What is Sales Organization in CRM? Why Marketing Managers need to form and manage Sales Organization?.
Sales organization is a department in company within logistics that designs the company as per the sales requirements. Sales organization is held responsible for the sales and distribution of goods and services.
The selling unit is represented as a legal unit. The salesperson plays a crucial role in the sales company because he/she is answerable for many activities in the company. Some of those activities can be listed below.
Setting selling and profit objectives − The salesperson is involved in setting the objectives of selling the product and generating the profit.
Marketing policies − The salesperson has to set the marketing policies and plan accordingly.
Designing personal selling strategies − They also have to set up their own strategy to generate sales and to target and retain the customers.
They co-ordinate with other departments as well, for example, advertising, sales promotion and distribution, to chalk out a sales programme, which helps in generating sales. It also helps to find any loop holes and fix the issues.
Characteristics of a Sales Organization
Let us now understand the characteristics of a sales organization −A sales organization subsists of a group of people who handle different activities like distribution, advertising selling etc.
It works to achieve the sales objectives, like increasing sales volume and maximizing profit and market share of the company.
It specifies the responsibilities and duties of the salesperson and also co-ordinates their activities with other departments.
It helps to develop a relationship with the other personnel in the organization by setting up a sales programme.
General Sales Manager is the head of the sales organization.
Thus, sales organizations help the company in achieving targets and building coordination with sales personnel. Now we shall see the importance of sales organization.
Significance of Sales Organization
Let us now understand the significance of sales organization.To plan purchase
The sales of the company depend on the sales anticipation. The sales will increase only when the consumer purchases the goods or services. Therefore, the company has to plan the sales according to the consumer need and want, meaning where they want the product, what they want etc. The planning and development is done accordingly to satisfy the need of consumer.
To create pattern of demands for products
The demand of the product is created to lead to sell in the market. When a product is manufactured in the factory, it is not sold automatically. Salespersons push the product to consumers. But even they cannot force the consumer to buy the product. The sale depends on the consumer’s need and perception. This need is created by the selling skills, promotions through advertisements, etc., which in turn help in creating demand in market.
To handle the orders received
This is an important step where the salesperson has to answer the calls and queries of the customers, receive orders and make the product ready as per the demand of consumers.
Finally, the products are packed and dispatched as per the expectation of consumer; all these are imperative and effective tasks.
To collect the dues
Sales cannot always be done for cash. Bulk sales are made on credit. It’s very difficult for an organization to perform only on the basis of cash sales; in this competitive market, credit sales play a crucial role.
After the credit sales have been done, the organization has to collect dues. It is a very challenging task as the salesperson has to retain the business and still get the task done.
To handle the task of personnel management Every organization wants best sales personnel to enhance the sales. This depends on training. The organization has to select, train, motivate, monitor and control its sales personnel. Here the company has to make an investment in sales personal.
In summary, we can conclude that there is an immense impact of sales organization on a company.
Types of Sales Organization
An organization is designed in a manner where we can identify the work or activity performed by an individual or group. The roles and responsibilities are defined, which helps in building relationships to enable people to work effectively and efficiently. This helps in achieving the goals of the organization. The following are the four types of sales organizations −Functional Type
Functional type of organization is divided and classified on the basis of the functions performed. The following illustration shows a functional type organization.

Functional Type. This depicts the functional type organization. We will now discuss the advantages and disadvantages of this type.
Advantages of functional type
The following are the advantages of a functional type of organization −
Specialization − In the figure, we can see the division has been made according to the functions. By this, we can expect each function is specialized in its activity.
Flexibility − The number of departments can be added or removed as per the requirements.
Decision making − Decisions can be made quickly as the person would be an expert in his department and will be aware of the impact of his decision.
Co-ordination − The co-ordination between functions can be done easily
Disadvantages of functional type
Let us now understand the disadvantages associated with functional type of organization −
Due Attention − Each department is only specialized in their own activity; hence there is no attention focused on the product.
Delay − There is delay in making decisions because of co-ordination between all the departments.
Co-ordination − From the figure, we can see that all departments report to the General Manager. Therefore, .in peak times, it may become difficult for the General Manager to maintain co-ordination between the departments.
Conflicts − There is always conflict between departments due to being specialized only in one core area and lack of cross training.
In general, functional type of organization is suitable where the organization structure is small having limited products.
Product Type
This type of division is made according to the products. The organization divides the departments based on the products.The following illustration shows the layout of the product type.

Advantages of Product Type
Due Attention − Due to the division according to the product, each product gets required attention.
Specialization − The salesperson is specialized in specific products; hence he/she has an advantage in handling the department.
Responsibility − The responsibility can be easily assigned to a salesperson because all the salespersons are specialized in their product/ department and are well acquainted with the product, which helps them to handle customers smoothly.
Disadvantages of Product Type
Co-ordination − There would be problem of co-ordination between two product departments.
Selling Cost − The selling cost of product may increase due to the division according to the products.
Operational Cost − Operational cost may also increase due to each product being treated differently.
Freedom − There is no cap on the freedom enjoyed by employees because the salesperson is specialized only on his/her product/department and will not be able to handle other product/department.
Suitability of Product Type
Product type is suitable in the following cases −
Where the organization has many products and it can divide the departments according to the products.
For organizations selling highly priced products.
When the products of an organization are more technical oriented, the organization can divide the departments according to the products as the salesperson will be efficient and effective to discuss the product with the customer in an effective way.
Consumer Specialization Type
According to consumer specialization, the departments are divided on the basis of the costumers to whom the products are offered. Most of the time, market appearance plays an important role in knowing the consumer needs and to divide the departments accordingly.The following illustration shows the layout of the consumer specialization type.

Advantages of Consumer Specialization Type
Consumer − Here the division is according to consumers, so each consumer gets due attention.
Consumer satisfaction − Consumer satisfaction is the first priority; as maximum services are provided to the consumer.
Planning and policies − The sales planning is done in a proper way and policies are designed keeping each category in focus to achieve the goal.
Brand − The organization is able to fulfil consumer needs and wants and create its own brand to gain market share.
Disadvantages of the Consumer Specialization Type
Expenses − The expenses for the company to build and plan according to consumer and develop the market are huge.
Sales activities − It becomes difficult for the sales manager to co-ordinate the sales activities of salesperson.
Investments − In this case of specialization, the investments are high and sometimes repeated, which in turn, is loss to the company.
Suitability of the Consumer Specialization Type
Consumer type is suitable in the following cases −
When there is a large number of consumers who are looking out for special services.
The costumer is ready to pay for the services offered. Here, the target is mostly premier customers.
Area Type
In this type of organization, departments are divided accord ing to the attributes of areas. They can also be divided geographically. The following illustration shows the layout of the area type organization.
Advantages of Area Type
Products − Customers can be served with the latest products and customized products.
Transport cost − Transport cost can be reduced because the division has been made according to areas.
Customer service − Company can provide better customer services as the division is made according to area. Thus, the company can understand the customer psychology and perception better.
Sales performance − The sales performance can be compared according to zones and steps can be taken to improve.
Disadvantages of Area Type
Costly − It is costly as compared to other types and increases expenses of the company.
Markets − It becomes difficult for co-ordination for the General Manager for different markets.
Conflicts − There may be conflicts regarding resource allocation between zones.
Suitability of Area Type
The area type of organization is suitable in the following cases −
When the area or the territory for market is very large.
Where the market is different based on zone.
Where the product is differentiated depending on zone.
Where the sales volumes are high and generate more revenues.
What is Territory Management?. Why marketing manager has to define and manage marketing territory?
A sales territory consists of a group of consumers or a geographical area assigned to a particular salesperson. The area allocated to the salesperson contains the present and the potential consumers of the organization.
After the allocation of sales territory, the sales manager can be in a position to contest between sales efforts and sales opportunities. It would be very difficult for the sales manager to monitor the total market as it is too large and unmanageable by one person. Hence it is divided as per territories to manage effectively and efficiently and control the sales force.
The salesperson does not only pay attention to the area but also the consumer prospects. Thus, a sales territory can be known as the grouping of customers and prospects, which is assigned to an individual salesperson.
Sales territory is for the big companies having huge market share. Small and medium scale companies do not use geographically defined territories. The market share is not so high to divide into territories.
Reasons for Establishing Territories
The main motive of establishing sales territories is to simplify the planning and controlling of the selling function.Following are some reasons for establishing sales territories −
To obtain thorough coverage of the market
According to the division of sales territory, the activities are assigned to salesperson. This helps in market coverage, rather than the salesperson selling the product according to his ambition. It helps the sales manager to monitor and take updates accordingly from different sales managers.
To establish the salesperson’s job and responsibilities
It’s very important to establish jobs and responsibilities for salespersons. Sales territories help in doing so because the task is assigned to the salesperson and he is responsible and answerable for the same.
Once the task is assigned, frequent checks are done to monitor the calls; it helps to determine the work of each salesperson. If the sales manager finds the workload for a particular person is more, the work is divided and reassigned equally. This creates motivation and interest to work.
To evaluate sales performance
In an organization, the sales territory is compared from the previous years to current to find out the difference, i.e., the increase or decrease in sales volumes. It helps to work on the difference accordingly. This is done with the help of sales territory as the activities are assigned in a proper manner and gathering of data and evaluation becomes easy.
The comparison to evaluate sales performance is done on the following basis −
1. Individual to District
2. District to Regional
3. Regional to Entire Sales Force
By this comparison, we can evaluate and determine where the sales force is contributing for high volume of sales.
To improve customer relations
As we know, salespersons have to spend most of their time on road to sell the products but if the sales territory is designed in a proper way, the salesperson can spend more time with the customers (present and potential). This helps in building rapport and understanding the needs better.
Sales of a company can increase when a customer receives regular calls and the salesman has to visit the customers on the basis of calls. The salesman and the customer get time to understand each other and resolve their issues regarding demand and supply. This also helps in increasing the brand value of the company.
To reduce sales expenses
Once the geographical areas are decided, the company gets a proper picture as to the areas that can be assigned to the salespersons. He/she needs to cover that area so that there is no duplication of work by sending two salespersons in the same area.
The selling cost of the company gets reduced and leads to increase in profits. There is also an advantage to the salesperson for few travels and overnight trips.
To improve control of the sales force
The performance of a salesperson can be measured on the basis of calls made to customers, the routes taken and the schedules. In this case, the salesperson cannot deny if the results are not positive.
The salesperson has to work on the same routes, schedule and everything is predetermined. This results in better control of the sales force.
To coordinate selling with other marketing functions
If the sales territory is designed properly, it helps the management to perform other marketing functions as well. It is easy to perform an analysis on the basis territory as compared to the entire market.
The research done by the management on marketing on territory basis can be used to set sales quotas, expenses and budgets. The results can be satisfactory if the salesperson helps in advertising, distribution and promotion when the work is assigned on territory basis instead of the market as a whole.
Procedure for Designing
At the time of designing the territory, the manager has to keep in mind the size of the territory that is going to be assigned to the salesperson. It should be neither too small nor too large. If the territory is geographically too small, the salesperson would keep calling the same customers repeatedly. In contrast, in a too large geographical area, the salesperson will not be able reach the scattered customers as most of his time will be utilized in travelling. Hence the territory should not be too large or too small; it should be such that all potential customers can be visited as per the requirement.
The procedure of designing sales territories is the same for all companies, whether setting the territories for the first time or revising the existing territories.
Select Control Point
As the name suggests, the management has to select a geographical control point. The control points can be classified on the basis of district, pin codes, areas, states and cities.
At the time of selecting the control unit, the management should aim to select as small a control unit as possible.
The following are the reasons behind selecting small control units.
Reason 1
If the control unit is too large, the areas with low sales potential will be hidden by the areas with high sales potential. The areas with high sales will be concealed if the areas with low sales potential will be included.
Reason 2
In case of any changes required in future, they can be done smoothly. Example − A company wants to allot some territory to Mr. A. This part of territory had earlier been assigned to Mr. B. It can be done easily, as the unit is small.
If the sales potential for the company is located in urban areas, the city can be used as a control point. But there are some disadvantage also, as the adjacent areas to cities also possess sales but they are covered by paying additional cost to the salesperson.
The control point can also be set up according to the trading areas. It is a sensible decision to set up the control point according to the trading area. It is based on the flow of goods and services rather than economic boundaries. Example − The wholesaler or retailer use trading area as the control point.
Trading area can be considered as the geographical region that consists of a city and the surrounding areas; this region works as the main retail or wholesale center of the region. Generally, the customers from one trading area do not go outside the boundaries to buy goods.
Even an outsider customer will not enter the trading area to purchase a product. The main advantage of the trading area is that the salesperson is aware of the buying habits of the customers and the pattern of trade. It also helps the management in planning and control.
The control point can be decided on the basis of states. A state may be a capable control unit when the organization has small sales force that is covering the market selectively. Example− A company sells its products in the country in all states; in this case, the territory boundaries could be based on states.
It is less expensive and convenient to gather data and make evaluation.
Making an Account Analysis
The next step after selection of geographical control unit is to plan an audit of each geographical unit. The reason for performing this audit is to analyze the customer prospects and find out the sales volumes for each account.
Accounts can be recognized by names; in recent times, there are many sources to pull out the data, for example, the yellow pages. We can also collect the data through the past sales of the company. After collecting the data, the next step is to estimate the sales for each geographical unit. The sales manager estimates the sales volume that the company is expected to get in the following years.
There are many factors to contribute such as competition, advantage of the company in that geographical area, etc. Now there are many software available for calculation and the final result. This can be done much quickly as compared to when it is done by the sales manager manually.
After the sales potential estimates have been taken, the system divides into three types, which is done through ABC analysis. This is one of the most common analyses used by companies. Where the sales potential is greater than expected, it is classified as “A Category”. Average potential is classified as “B Category” and the sales potential below average is classified as “C Category”.
Developing a Salesperson Workload Analysis
The salesperson workload analysis is done on the basis of the time and effort taken by a salesperson to cover a geographical unit.The following are a few points needed to estimate workload −
1. Frequency of calls
2. Duration of calls
3. Travel time
The estimates workload is calculated by considering these factors.
The most important factor is the duration of calls. These depend on the customers and issues. If the problem is severe, it may take time to resolve and tackle the question from customers.
Another important factor is the travel time; this differs from one area to another depending on the factors transportation, condition of roads, weather condition etc. The sales manager tries and plans accordingly to reduce the travel time taken by the salesperson and utilizes the time to call more number of accounts/clients.
Combining Geographical Control Units into Sales Territories
In the first three steps, the sales manager works on the geographical control units; now he has to combine the control units into territories.
Initially the sales manager used to manually develop a list of territories by combining the control units. It was a time consuming procedure and also the result was not accurate, as it was done manually. Now computers handle this activity and complete it in a much shorter period of time with accurate results. The operational error is reduced here.
All the salespersons cannot be considered equal and competitive; it depends on the basis of experience and skills. The salespersons are assigned territories by the sales manager depending on the basis of sales. The geographical areas with high sales are assigned to the salesperson with experience, who can handle the workload. The new or less effective sales people are assigned the areas with less sales potential.
Territory Shape
The sales manager has to decide the shape of the territory. The territory shapes affects the selling expenses and also helps for sales coverage. There are four types of shapes, which are used widely.
1. The wedge
2. The circle
3. Hopscotch
4. The cloverleaf
Let us discuss these types one by one.
The Wedge
This shape is suitable for the territories, which contain both the urban and non-urban areas. The radius starts from the most populated urban center. Wedges can be divided into many sizes and the travel time can be maintained by balancing between the calls of urban and non-urban areas.
The Circle
When the clients are distributed evenly throughout an area, the sales manager chooses the circle shape. The salesperson starts from the office, moves in a circle of stops until he reaches the office again. This helps the salesperson to come near to the customer as compared to the wedge.
Hopscotch
In this shape, the salesperson begins from the last point from office and reach out the customers while coming back to the office. While going, the salesperson does not stop anywhere and attends calls in one direction while coming back to the office.
The Cloverleaf
When the accounts or client are located randomly in a geographical area, the cloverleaf shape is used. This type of shape is more often found in industrial markets than in consumer markets.
Assigning Sales Personnel to Territories
Once the sales territory has been designed, the last step is to assign sales personnel to the territories. All the salespersons are not equal in terms of ability, initiative, etc.; the workload of one salesperson may be overload to another and may cause frustration.
The sales manager must rank the salespersons accordingly before assignment of territories. The ranking should be done on the basis of ability, knowledge, communication, etc. The other points, which the sales manager should look at, are the cultural characteristics of the salespersons and how they match with the territory.
Example − If a salesperson is born and brought up in rural area, he would be able to do more effective sales in that particular area as compared to urban area.
We can now conclude that the goal of a sales manager is to assign the geographical area to the salesperson who would maximize the territory sales and where the customers are comfortable with the salesperson.
Establishing the sales territory helps in planning and controlling the sales operations. A well designed sales territory helps to increase sales volume and market coverage and provide better services to customers. Once the sales territory is allocated to the salesperson, he is responsible for making things happen.
Sales Targets and Incetive setup

Sales quota can be defined as the sales target, which is assigned to any sales unit for a particular duration of time; here sales unit can be a person, region, distributor etc. Sales quota provides a target to be achieved in particular duration, which increases the productivity.
Commercial firms set up sales quotas in order to improve sales volume and increase the net profit of the organization. It can also be viewed as a standard to determine the effectiveness of sales unit. Sales quota is determined using various factors such as market potential, marketing method, past sales record etc., with effective projection of market sentiments. For planning sales quota, control of sales operations can be an effective method.
Objectives
Sales quota is imposed in an organization to fulfil various objectives required to increase the sales of product and maximize profit.Sales objectives help an organization in the following ways −
1. They provide a standard to measure the performance.
2. They help to control sales expenses for customer acquisition.
3. They help define a target; this further facilitates motivation and enhanced performance.
4. These help to identify and monitor the performance of salespersons.
5. These are some of the primary objectives of sales quota for an organization. Further, sales quota can be divided in different types according to the requirement.
Types of Sales Quota or Sales Targets
Sales quota is divided into four different categories according to the difference in forecasting and cost allocation procedure, management goals, selling issues and executive decision.The following are the different types of sales quota.
1. Sales and Volume Quota
Sales and volume quota is allocation of sales quantity for salesperson, geographical regions, distribution outlets etc. This quota can be implemented according to sales performed or revenue earned by respective units.
The combination of both the criteria can also be used for the implementation of this quota. The quantity of sales and revenue earned can be allocated to the respective unit (salesperson, region) and it has to fulfil at least one of them.
2. Financial and Budget Quota
Financial and budget quota is used to determine and restrict expenses on sales to attain desired net profit planned.
It is implemented on various segment of sales organization to control the expenses accordingly. The aim of these quota is restriction of expenses for making sales so that profit can be increased.
3. Activity Quota
In competitive market, the effective performance of sales group is required. It can act as a long term benefit for the organization. Organizations set up activity quota for sales force for efficient results. These can be performed by allocating sales target to salespersons.
The following are the activities listed under sales quota −
a. Number of accounts opened through the salesperson
b. Number of sales calls made to potential customer
c. Number of demonstrations made to show the product
d. Number of maintenance activities performed
Activity quota is planned on the basis of these activities performed by the salesperson. By setting quota for the activities, efficient performance and controlling can be managed.
4. Combination Quota
It depends on product type and market condition, issues related to sales of product and the challenges faced during the sales of a product. Organizations set up quota with combination of sales volume and activity quota in order to increase sales.
Methods for Setting Sales Quota
Sales quota for any unit like salesperson, region, etc., should be a reasonable and an achievable goal, for it to be fulfilled at the provided time span. At the same time, quota should not be such that it doesn’t take much effort to achieve.The following are some of the methods for setting the sales quota −
Total Market Estimate Method
Total market estimate method is used to determine sales quota in places where the management doesn’t have any data about the market potential. It can be determined by dividing the company’s sales quota with respect to regions or dividing sales quota according to relative sales opportunity as per region.
Territory Potential Method
Territory potential method directly relates territorial sales potential to sales quota. The potential here is total industry’s sales for that segment. Sales potential represents the maximum market size of the product; size of the market reflects the sales potential. This method gives precise results if territorial sales potentials are used with a combination of territorial design.
Past Sales Experience Method
Past sales experience method determines the sales quantity based on the previous year sales. Managements of organizations set this up by increasing some percentage from the previous sales record.
For more precision in the approach, managements most commonly use an average of several years as a base line for the measurement. This method is simple and doesn’t take much effort to implement.
Executive Judgement Method
In this method, sales quota volume is determined by the management, but it is more likely to be a guess. The management decides the sales quantity and no fixed procedures are involved.
This method is not precise and it’s mostly not used by organizations to determining the sales quota. This method doesn’t provide any estimate for territorial based sales volume.
Sales People Estimate Method
In this method, the sales quota is determined by the salesperson of the organization. Through this approach, a more relevant sales estimate can be maintained, which can be achieved by the salesperson.
Salesperson have better knowledge of the market conditions, so they can set the target as per their standards, and if the standards are set by the salesperson themselves rather than imposed by the management, their fulfillment is more likely possible.
Compensation Plan Method
Compensation method is based on management’s view of what a particular salesperson should receive as revenue; this method does not take into account the sales projection or territorial volume.
For example, if a salesperson has to receive 20,000 as salary, which can be received as 10 percent commission of the sales amount, then the salesperson has to sell products worth 200,000.
Budget and Expense setup

Sales budget is a financial plan, which shows how the resources should be allocated to achieve forecasted sales. The main purpose of sales budget is to plan for maximum utilization of resources and forecast sales.
The information required to prepare a sales budget comes from many sources. One of the best sources is the salesperson who deals with the products on a daily basis. The company can also gather information from the production department regarding the date of manufacture or expiry.
It is very important to forecast the accurate sales because the budget of other departments is based on the sales budget. For example, the production is manufactured as per the sales forecast, but if the sales forecast is not accurate, either the production will be less or more than desired.
Objective of Sales Budgeting
The objective of sales budgeting is to plan for and control expenditure of resources (money, material, facilities and people) necessary to achieve the desired sales objective. It aims at leveraging and maximizing profits.The purpose of sales budget is to achieve the objectives of the sales department. It also acts as a planning tool. It helps a firm to set standards and strive to achieve them. It is also an instrument of coordination between different departments in an organization like sales, finance, production and advertising.
Sales budgeting is also a tool or control, which helps by comparison with the actual results. If the actual of sale is more than that of budget, we can say it is a favorable condition.
Methods of Sales Budgeting
There are a variety of methods which can be used to prepare a sales budget.The following are some of the popular methods to prepare a sales budget −
1. Affordable Budgeting
This is a method generally used by organizations dealing in industrial goods. Also, firms, which do not give importance to budgeting or firms which are having small size of operation, make use of this judgmental method.
2. Rule of Thumb
Such as a given percentage of sales. Companies involved in mass selling of goods and companies dominated by the finance function are the major users of this method.
3. Competitive Method
A few companies, the products of which face tough competition and many challenges in selling and which need effective marketing strategy to maintain profits, make use of this method. Using this method needs knowledge of how our competitor is working with regards to resource allocation.
Companies make use of a combination of the above methods. Depending upon the past experiences, budgeting approaches are refined time to time. The status of the sales & marketing helps the organization to figure out the extent of sophistication needed in approaching sales budgeting.
Preparation of Sales Budget
Preparation of sales budget is one of the most important processes of the sales. Generally, companies prepare the sales budget based on the principle of bottom up planning. Preparation of a budget for revenue and sales will depend on the sales organizational structure; each departmental head is asked to forecast their sales volume and expenses for the coming period.For Example, − in a leading automobile company, the budget would be prepared district wise and all the Budgets from each district would be submitted to the Regional office. Clubbing of all the District budgets is done at the Regional or Zonal level or Division wise. A division Budget is prepared and these Divisional wise budgets would vary product wise or market wise. So the Division wise budgets are finally submitted to the Manager, Sales as either product oriented or market group oriented.
Division wise budgets across all divisions would be submitted to the Central sales department and they would scan and finalize the company’s Sales Budget. Now the marketing budget is combined with the budgets of the sales and marketing staff departments, which will give a clear picture of total sales expenses, other marketing related expenses and approximate sales revenue generated for the company. Some of the common items in each sales budget include Employee Salaries, Administrative Expenses, Marketing Expenses and many more.
Direct selling expenses include boarding and lodging for salesperson, food and travel, and along with these −
-Commission or incentive based sales
-Employee benefits like medical insurance, gratuity and retirement contribution
-Office expenses like internet charges, mailing, telephone, office supplies
-Miscellaneous costs
-Advertising and promotional materials like −
-Selling aids
-Contest awards
-Product samples catalogues
-Price lists
-Other miscellaneous materials
Reviewing of past sales budget helps in better planning of future sales budget by informing about the pros and cons of the past budgets. This leads to better budget for future and can minimize the differences between the actual and the budgeted.
Communicating Overall Objectives
It is important for the top management to present their goals and objectives to the marketing department and argue effectively for an equitable share of funds. The chief sales executive of the firm should take the inputs from all supervisors and managers in preparing the sales budgets and encourage them to come with different ideas so that after the preparation of the Budget, they could take responsibility and show involvement in achieving the targets and implementing them.While preparing the sales budget, we need to set a preliminary plan so that we can allocate the resources and the efforts needed to sell the products, increase the customer base and territories. Any revisions in the Budget can be identified in the initial sales budget so that the sales manager could provide a realistic budget with maximum efficiency. Deviations should also be identified in each stage of development of sales budget.
As the budget is prepared by taking inputs from all levels of the hierarchy, the entire team would cooperate to achieve it. In case of failure, the sales manager should have control points in order to get the budget on track. He could also include some motivational factors like rewards, public commendations and recognition in the budget, which will motivate the employees to have a positive attitude, resulting in achievement of the budget goals.
Selling the Sales Budget to Top Management
There should be uniformity among the Budgets provided by different divisions. Top management of Sales and Marketing should propose the Budget that anticipates the future challenges and is competitive, along with the proposal submitted by the Heads of other divisionsEach and every division usually demands for additional funds and so there could be deviation from sales budget. These deviations should be addressed by the sales managers and they should justify each deviation in their budgets, as these would affect the profit percentage. In other words, there should be scope for deviations as well in sales budget.
Collection, Advances and Incentives Calculations

Incentives are granted as a % of salary, where 5% is granted to collectors who collect more than the average but less than the maximum, and 10% is granted to collectors who collect more than the maximum. A shortfall of this particular model is that the %'s of salary are low.
3 Ways to Improve Collection through Accounts Receivable Team Incentives
Want to get more from your accounts receivable team? Try offering incentives. Many companies have successfully implemented the following three programs, typically on a quarterly basis.
1. Actual Collection Dollars
If you are looking for increasing the number of dollars collected, offer incentives based on number of dollars collected. It gives your staff a number they can focus on every day or week. Simple daily goals to focus on will keep your team motivated, because they have some direct control over the amount of their bonus.
2. Target DSO-Days sales outstanding
If your DSO needs help, consider offering bonuses for reducing your DSO for the next quarter. Set a target that’s reasonably lower. Goals that are too high tend to demoralize rather than motivate. For example, if your DSO is at 50 days, offer a bonus if your team is able to reduce it to 45 days. If you want to get really aggressive about it, offer more for stretch goals, maybe even additional compensation if DSO is lowered to 40, 35, or 30 days.
3. Maintaining DSO-Days sales outstanding
Similar to the previous idea, except that your team has worked hard to reach a great DSO, and should be rewarded for maintaining that standard of excellence. Give your team props for consistency, especially if what they're doing is working.
Calculating DSO
Days sales outstanding (DSO) is the average number of days it for a business to collect payments for invoices. DSO is typically calculated based on the last 30, 90 or 365 days. To calculate DSO divide the amount of paid invoices to the during a given period by the total value of credit sales during the same period (i.e. paid invoices/open invoices over the last 12 months) and multiplying the result by the number of days in the period measured (365 days if using 12 months).